In the intricate tapestry of the internet, where every click and scroll tells a story, there exists a group of silent orchestrators. These individuals and companies play a pivotal part in shaping the landscape of online commerce, though their presence is often felt more than seen. They are the unseen guides who help tailor the digital experiences we encounter daily, BlockShopper removal request ensuring that the advertisements we see are not just random, but relevant.
This section delves into the complex world of these information intermediaries, exploring how they collect, analyze, and sell valuable insights. Their work is fundamental in the realm of electronic commerce, where understanding consumer behavior is key to effective promotion and sales. By examining their methodologies and ethical considerations, we gain a deeper understanding of the mechanisms that drive personalized advertising and its implications for privacy and consumer rights.
Understanding the Dynamics: These intermediaries operate at the intersection of technology and consumer data, acting as the bridge between vast pools of information and the companies seeking to harness this data for targeted campaigns. Their role is crucial in a market where competition is fierce and the ability to reach the right audience at the right time can make or break a campaign.
Navigating Ethical Waters: As we explore the practices of these information handlers, it becomes imperative to consider the ethical dimensions of their operations. The balance between providing tailored experiences and respecting individual privacy is a delicate one. This discussion is not only about the tools and techniques used but also about the broader societal impact of these practices.
In conclusion, this exploration into the world of these silent architects of online advertising not only sheds light on their significant role but also prompts us to reflect on the future of personalized marketing and the safeguards needed to protect both businesses and consumers in an increasingly data-driven world.
Understanding Information Intermediaries

This section delves into the various techniques employed by information intermediaries to gather and manage consumer details. It explores the methodologies that are central to their operations, highlighting both the technological and human aspects involved in the accumulation of personal information.
- Online Tracking: Information intermediaries often use cookies and similar technologies to monitor user activities across websites. This helps in building a detailed profile of individual browsing habits and preferences.
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Direct methods such as surveys and questionnaires are frequently used to collect specific information from consumers. These tools allow intermediaries to gather detailed demographic and psychographic data.
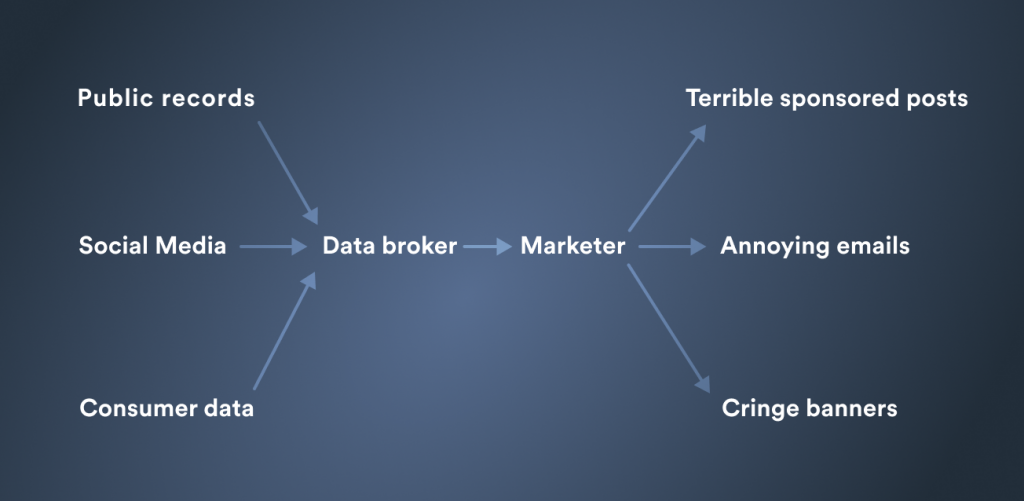
- Public Records Analysis: Accessing and analyzing public records such as property deeds, court records, and professional licenses can provide a wealth of information about individuals.
- Social Media Mining: With the widespread use of social media, intermediaries can extract a significant amount of personal information from user profiles and interactions on platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn.
- Transactional Data Collection: Information from financial transactions, including credit card purchases and online shopping habits, is another rich source of data for intermediaries.
- Mobile Device Tracking: The use of mobile apps and location services allows intermediaries to track physical movements and habits, providing insights into consumer behavior and preferences.
- Third-Party Data Acquisition: Intermediaries often purchase data from other organizations, including market research firms, credit agencies, and data aggregators, to supplement their own datasets.
Each of these methods plays a crucial role in the comprehensive data collection strategies employed by information intermediaries. Understanding these techniques is essential for consumers and regulators alike, as it sheds light on the extent and nature of personal information being collected and utilized in the modern marketplace.
Data Collection Methods
This section delves into the various techniques employed by entities to gather information from users across online platforms. These methods are pivotal for creating personalized experiences and targeted communications, but they also raise significant privacy concerns.
One common approach involves tracking user interactions with websites and applications. This can include monitoring clicks, views, and purchases to build detailed profiles of individual preferences and behaviors. Another method is the use of cookies and similar technologies that store small pieces of information on users’ devices to remember their actions and preferences over time.
Additionally, many platforms integrate third-party services that collect data from multiple sources to enhance the depth and breadth of the information available. This cross-referencing of data allows for more nuanced insights into consumer behavior and market trends.
Furthermore, some entities employ data mining techniques to analyze large sets of information for patterns and correlations. This advanced analysis can reveal trends that are not immediately apparent, providing a competitive edge in the marketplace.
While these methods offer significant benefits in terms of personalization and efficiency, they also necessitate careful consideration of privacy regulations and ethical standards to ensure that user information is handled responsibly and securely.
Data Privacy Concerns
This section delves into the critical issues surrounding the confidentiality and security of personal information gathered and utilized in the realm of online promotion. As entities engaged in the collection and sale of user details become more prevalent, the need for robust frameworks to protect consumer privacy grows increasingly urgent.
In the current digital landscape, numerous regulations have been established to address these concerns. These frameworks aim to ensure that the acquisition, storage, and dissemination of sensitive information are conducted in a manner that respects individual rights and adheres to legal standards. Key among these are laws designed to enforce transparency, consent, and accountability in the handling of personal data.
One of the primary challenges in this area is the global nature of the internet, which complicates the enforcement of privacy laws across different jurisdictions. This necessitates a harmonization of regulations to create a cohesive global standard that can effectively safeguard user information regardless of geographical boundaries.
Furthermore, the rapid evolution of technology presents ongoing challenges to regulatory frameworks. As new methods of data collection and analysis emerge, it becomes essential for these regulations to be adaptable and forward-thinking, capable of addressing emerging threats and protecting consumers from potential misuse of their personal information.
Ultimately, the establishment and enforcement of comprehensive regulatory frameworks are crucial in maintaining consumer trust and fostering a healthy environment for online promotion. By ensuring that privacy concerns are adequately addressed, these frameworks not only protect individuals but also promote ethical practices within the industry.
Regulatory Frameworks
This section delves into the legal structures designed to oversee and control the collection, usage, and dissemination of personal information in the realm of online advertising. These frameworks are crucial for ensuring that consumer rights are protected and that the practices of information intermediaries align with ethical standards.
Several key regulations have been established to govern these practices:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Enforced by the European Union, this regulation sets high standards for consent and data protection, impacting any organization that handles EU citizens’ personal information.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): Similar to GDPR, this law grants California residents significant rights over their personal data, including the right to know what information is collected and the right to opt-out of its sale.
- Federal Trade Commission (FTC) Regulations: The FTC plays a pivotal role in monitoring deceptive practices and ensuring that companies adhere to fair information practices.
These regulations not only dictate how personal information can be used but also impose stringent requirements on transparency and accountability. For instance, companies must clearly disclose their information practices and obtain explicit consent before collecting sensitive information.
Moreover, the enforcement of these regulations has led to the development of new technologies and practices aimed at enhancing privacy. These include anonymization techniques, encryption methods, and the implementation of robust consent management platforms.
In conclusion, regulatory frameworks are essential in maintaining a balance between the benefits of targeted advertising and the protection of individual privacy rights. As technology evolves, so too must these regulations to keep pace with new challenges and threats to privacy.
Targeted Advertising
Targeted advertising represents a strategic approach in the realm of promotional activities, focusing on delivering personalized messages to specific segments of the audience. This method leverages collected information to enhance the relevance and effectiveness of ad campaigns, ensuring that the right message reaches the right people at the right time. By analyzing various factors such as demographics, browsing habits, and purchase history, advertisers can craft messages that resonate more deeply with potential customers, thereby increasing the likelihood of engagement and conversion.
The essence of targeted advertising lies in its ability to refine the audience based on detailed insights. This precision allows for a more efficient use of advertising budgets, as ads are directed towards individuals who are more likely to be interested in the product or service being offered. Moreover, this approach not only benefits the advertisers by improving their return on investment but also enhances the user experience by reducing the clutter of irrelevant advertisements.
However, the effectiveness of targeted advertising is not solely dependent on the collection and analysis of information. It also requires a deep understanding of consumer behavior and the ability to adapt to changing trends and preferences. As technology advances, the methods of data collection and the algorithms used for targeting continue to evolve, offering new opportunities and challenges for advertisers. Balancing the benefits of personalized advertising with the ethical considerations and privacy concerns remains a critical aspect of this field.
In conclusion, targeted advertising stands as a pivotal strategy in the modern advertising landscape, driven by the continuous evolution of data analytics and consumer insights. Its ability to connect with audiences on a more personal level not only enhances the efficiency of advertising efforts but also sets the stage for a more interactive and responsive marketing environment.
Data Broker Services
This section delves into the array of services offered by entities that aggregate and sell information. These services play a crucial part in shaping consumer interactions and market dynamics. By examining the various offerings, we can better understand how these entities influence the marketplace.
Information aggregators provide a wide range of services that cater to different aspects of consumer behavior analysis and market targeting. These services are designed to enhance the effectiveness of advertising campaigns and improve customer engagement strategies.
| Service Type | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Profiling | Creating detailed profiles based on collected information to understand consumer preferences and behaviors. | Enhances targeted advertising by providing specific insights into consumer interests. |
| Market Segmentation | Dividing the market into distinct segments based on demographic, psychographic, and behavioral data. | Helps in tailoring marketing strategies to specific segments, increasing effectiveness. |
| Risk Assessment | Analyzing data to assess potential risks associated with consumer behavior or market trends. | Aids in mitigating risks and planning strategic responses to market changes. |
| Data Integration | Combining data from various sources to provide a comprehensive view of consumer behavior and market trends. | Improves data accuracy and reliability, leading to better decision-making. |
The services offered by information aggregators are pivotal in modern commerce, enabling businesses to make informed decisions based on accurate and detailed consumer data. This not only enhances marketing strategies but also fosters a more personalized consumer experience.
Impact on Consumer Behavior
This section delves into how the collection and utilization of information by intermediaries in the online advertising industry influence the actions and decisions of end-users. By examining various scenarios and outcomes, we aim to understand the profound effects these practices have on consumer conduct.
The manipulation of consumer preferences through targeted ads is a significant area of concern. Intermediaries often use detailed profiles to tailor advertisements, which can lead to a skewed perception of market offerings. This practice not only influences immediate purchasing decisions but also shapes long-term consumer habits and brand loyalty.
| Aspect | Impact |
|---|---|
| Immediate Purchasing Decisions | Targeted ads can significantly increase the likelihood of a purchase by appealing to specific interests or needs. |
| Long-term Consumer Habits | Repeated exposure to tailored ads can reinforce certain buying patterns, leading to long-term brand allegiance or dependency on certain products. |
| Market Perception | Consumers may develop a biased view of available products and services, influenced by the selective exposure to advertisements. |
Furthermore, the ethical implications of such practices are vast. The potential for creating a marketplace that caters more to the interests of advertisers than to the genuine needs of consumers raises important questions about fairness and transparency in the industry.
In conclusion, the influence of intermediaries on consumer behavior is multifaceted, affecting not only individual purchasing decisions but also broader market dynamics. As technology advances, it is crucial to consider the ethical dimensions of these practices to ensure a balanced and fair marketplace for all participants.
Ethical Considerations
Navigating the moral landscape of information intermediation is crucial as the industry evolves. This section delves into the ethical dilemmas that arise when handling and disseminating personal details, emphasizing the need for transparency, consent, and fairness in all operations.
One of the primary concerns revolves around informed consent. Users must be fully aware of how their details are being used and for what purposes. This involves clear communication and accessible privacy policies that are not only legally compliant but also easily understandable by the general public.
Another significant ethical consideration is the potential for discrimination. Using personal details to target specific demographics can lead to biased practices, particularly if the targeting is based on sensitive attributes such as race, religion, or health status. Ensuring that practices do not perpetuate inequality is essential.
Transparency is also a key ethical pillar. Companies must be open about their methods of collection and usage of information. This not only builds trust with consumers but also aids in maintaining a clear conscience in the industry.
Lastly, the concept of fairness in compensation and control over personal details is paramount. Users should have the right to opt-out or modify how their details are used, and in some cases, be compensated for the use of their information, especially when it generates significant revenue for intermediaries.
In conclusion, as the field of information intermediation continues to grow, it is imperative that ethical standards are not just met but exceeded. By prioritizing the rights and interests of individuals, the industry can ensure sustainable and responsible growth.
Future Trends in Data Brokering
As the landscape of information intermediation continues to evolve, several emerging patterns are reshaping how stakeholders interact and leverage collected insights. This section delves into the anticipated developments that could redefine the industry’s operational and strategic approaches.
One of the most significant shifts is the integration of advanced analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) into traditional information intermediation services. This integration promises to enhance the precision and efficiency of targeted advertising campaigns, enabling more personalized consumer interactions. AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets to predict consumer behavior and preferences, leading to more effective marketing strategies.
- AI and Machine Learning: The adoption of AI and machine learning technologies is set to revolutionize how collected insights are processed and utilized. These technologies can identify patterns and trends that are not apparent through traditional analysis methods, providing a deeper understanding of consumer behavior.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain offers a secure and transparent way to manage and share information, which could significantly impact the privacy and security aspects of information intermediation. By ensuring that data transactions are traceable and immutable, blockchain technology can enhance trust among consumers and marketers.
- Increased Regulatory Scrutiny: As concerns over privacy and data misuse grow, regulatory bodies are expected to impose stricter guidelines on how information is collected and used. This trend will necessitate more robust compliance measures and ethical data handling practices.
- Collaborative Ecosystems: The future of information intermediation is likely to involve more collaborative efforts between various stakeholders, including marketers, technology providers, and regulatory bodies. These partnerships will aim to create a more integrated and efficient market for consumer insights.
- Focus on Consumer Consent: There is a growing emphasis on obtaining explicit and informed consent from consumers regarding the use of their personal information. This shift will likely lead to more transparent practices and possibly new models of compensation for consumers who share their data.
In conclusion, the future of information intermediation is poised to be marked by technological advancements, heightened regulatory oversight, and a greater emphasis on ethical practices. These trends will not only influence how information is managed but also redefine the relationship between consumers and those who facilitate the use of their personal insights in marketing efforts.
Collaboration with Marketers
In the realm of online advertising, the synergy between information intermediaries and promotional strategists is pivotal. This section delves into how these two entities work in tandem to enhance campaign effectiveness and consumer engagement. By exploring the mutual benefits and challenges of this partnership, we aim to provide insights into optimizing collaborative efforts.
Marketers often rely on the insights provided by information intermediaries to refine their strategies. These intermediaries offer a wealth of demographic and behavioral insights that can be crucial in tailoring promotional content to specific audiences. The collaboration typically involves sharing of anonymized user data, which helps marketers in creating more personalized and effective advertising campaigns.
However, this partnership is not without its complexities. Ensuring compliance with privacy regulations and maintaining ethical standards are paramount. Marketers must navigate these challenges carefully to avoid potential pitfalls such as consumer backlash or legal repercussions. Effective communication and clear agreements between both parties are essential to mitigate these risks.
Looking ahead, the integration of advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning could further enhance the collaboration. These tools can help in analyzing vast amounts of information more efficiently, leading to more precise targeting and better consumer insights. As the landscape of online advertising continues to evolve, ongoing collaboration and innovation will be key to staying ahead.
In conclusion, the partnership between information intermediaries and promotional strategists is a dynamic and essential component of modern advertising strategies. By fostering a robust and ethical collaboration, both parties can achieve greater success in reaching and engaging with their target audiences.
